Ever struggled with distorted audio or annoying background noise in your recordings? Chances are, your microphone gain settings are off! Whether you're recording a podcast, filming a video, or hosting a virtual meeting, getting your mic gain right is the key to clear, professional sound. This ultimate guide takes you from beginner basics to pro-level tips, helping you master microphone gain settings, eliminate background noise, and achieve studio-quality audio. Ready to make your voice shine? Let’s dive in!
What Is Microphone Gain?
Curious how your mic turns whispers into clear audio? Microphone gain amplifies the weak sound signal captured by your mic to a level suitable for processing or output. Measured in decibels (dB), it’s adjusted via your audio interface, mixer, or mic’s knob.
- What it does: Boosts quiet sounds without adding too much noise.
- Why it matters: Proper gain prevents distortion or excessive background noise, ensuring balanced, professional audio.
What’s the Difference between Gain and Volume
Ever mixed up gain and volume? They’re often confused, but they play different roles in your audio setup.
- Gain: At the input stage, it amplifies the raw signal. Too high causes distortion; too low boosts noise.
- Volume: At the output stage, it controls playback loudness without affecting signal quality.
| Aspect | Gain | Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Input (mic/interface) | Output (speakers/software) |
| Impact | Amplifies signal, may add noise or distortion | Adjusts final loudness, no quality impact |
| Common Issues | Clipping or noise | Speaker damage from excessive loudness |
| Best Practice | Target peak -18dB to -6dB | Adjust for environment |
Quick Tip: Next time you record, tweak gain first, then volume to keep your signal chain clean! See our guide on AI noise cancellation for advanced audio clarity tips.
Why Proper Gain Settings Are Critical
- Avoid Clipping and Distortion: High gain causes “crackling” that ruins audio.
- Optimize Signal-to-Noise Ratio: Low gain amplifies background noise, reducing clarity.
- Protect Gear: Overly strong signals can damage audio interfaces or mixers.
How to Set Microphone Gain
Prep Work: Create the Perfect Recording Environment
Want pro-level audio? Start with a solid recording setup! Here’s how:
- Silence Is Golden: Pick a quiet room and use soundproofing materials (like foam panels or blankets) to cut environmental noise.
- Mic Placement: Keep the mic 6-12 inches from the source, using proximity effect for richer bass (great for podcasts).
- Gear Setup: Connect your mic to an audio interface or computer, ensure drivers are installed, and secure cables. Turn off monitoring to avoid feedback.
Core Steps: Nail Gain Settings in Three Steps
Tired of inconsistent audio levels? Follow these three steps to set gain like a pro:
- Test Normally: Speak or sing at your typical volume, mimicking your actual recording scenario (e.g., casual tone for podcasts, max volume for music). Watch the VU meter.
- Monitor the Meter: Check the input level in real-time, understanding dBFS (decibels full scale), where 0dBFS is the max limit.
- Adjust the Gain Knob: Slowly increase gain until peaks hit -18dB to -6dB, avoiding the red zone (clipping). Use gain staging in software like Audacity or OBS for consistency. Record a sample and playback to check for distortion or weak signals.
Quick Tip: Setting wireless microphone gain settings is a breeze with user-friendly systems like the BOYA Magic. Simply sync the transmitter and receiver gain to avoid signal loss, and use the BOYA APP Center to fine-tune levels with a few taps, perfect for vloggers and podcasters who need quick, reliable setups.
To avoid clipping entirely, consider using a safety track as a backup or explore 32-bit float recording to eliminate manual gain adjustments.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Made these gain-setting errors? Here’s what to watch out for:
- Mistake 1: Lower gain means less noise? Wrong! Too low amplifies later-stage noise.
- Mistake 2: Crank gain for loudness? That’s a recipe for distortion.
- Mistake 3: Focus only on volume? Prioritize gain to get it right.
Rule of Thumb: Better quiet than distorted—always leave headroom!
Advanced Gain Settings
Gain and Noise: How to Tackle Background Noise
Annoyed by background noise ruining your recordings? Try these tricks:
- Pick the Right Polar Pattern: Cardioid cuts side noise for podcasts; omnidirectional captures ambient sound for group talks.
- Use a Noise Gate: With proper gain, it mutes low-level noise, keeping audio clean.
- Optimize Your Space: Add sound-absorbing materials (like acoustic foam or curtains) and adjust mic placement.
Gain for Different Mic Types
Did you know your mic type affects gain settings? Here’s the breakdown:
- Dynamic Mics: Low sensitivity, need higher gain, ideal for music (drums, guitars).
- Condenser Mics: High sensitivity, lower gain needed, great for podcasts or vocals.
- USB Mics: Gain often adjusted in software, user-friendly for beginners.
- Wireless Mics: Sync transmitter and receiver gain to avoid signal loss.
Gain and Effects: The Role of Preamps
- Microphone Preamp: Delivers clean gain, the first step in a pure signal chain.
- Compressor: Post-gain, it controls dynamic range to prevent peak overloads.
Microphone Gain Settings for Different Use
Struggling with gain in specific setups? Here are tailored tips for top scenarios!
Outdoor Interviews and Video Shoots
Battling wind noise outdoors? Outdoor settings have wind and ambient noise, so keep gain conservative.
- Key Tips: Use a windscreen to block wind noise and enable a high-pass filter (HPF, cutting 75-80Hz). Aim for average peaks at -12dB to handle sudden loud sounds.
- Mic Placement: Keep 6-12 inches from the source, facing away from wind to avoid vibrations.
- Pro Tip: Test with a wireless mic and simulate real interviews to check wind noise.
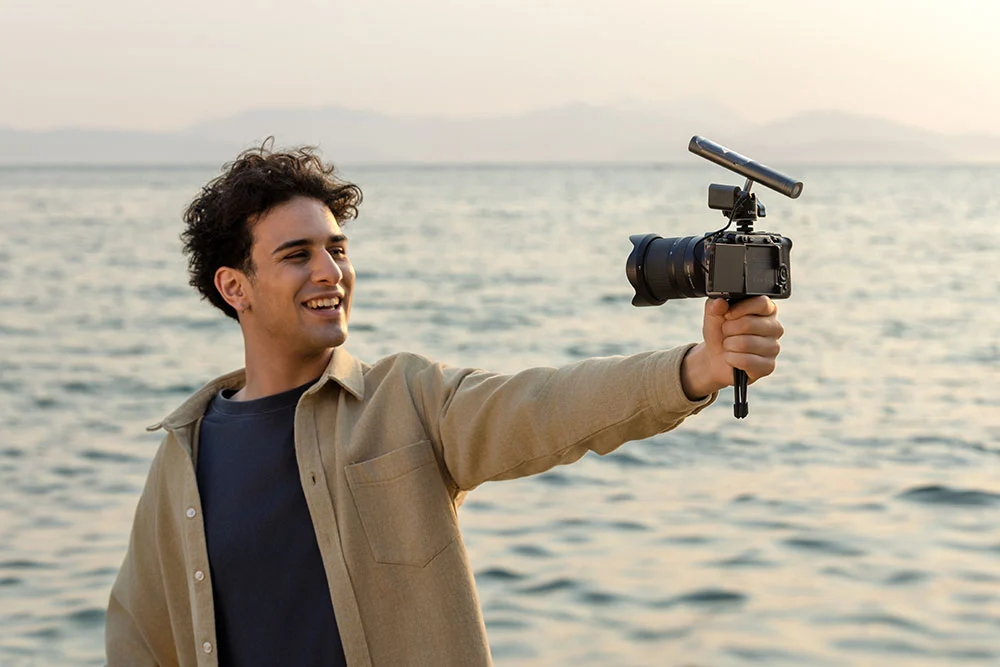
Recording Video with a Camera
Camera audio levels jumping around? It might be auto-gain control (AGC) causing trouble!
- Key Tips: In manual mode, set camera gain to minimum and use the mic’s +20dB boost. Target -12dB peaks to avoid clipping.
- Mic Placement: Use a long cable (e.g., 10ft XLR) and angle slightly off-axis to reduce pops.
- Pro Tip: Monitor with a VU meter to stay below 0dB. Perfect for vlogs, prioritizing clean signals.

Podcasts and Live Streams
Want your podcast to sound pro? Start with gain settings!
- Key Tips: Set gain for peaks at -3 to -1dB or average -12dB. Use gain staging to avoid amplifying noise later, and add a noise gate with light compression (2:1 ratio).
- Mic Placement: Maintain fist distance (about 6 inches) and use a pop filter to reduce plosives.
- Pro Tip: Test in a quiet room. For multi-person podcasts, adjust each mic’s gain individually.
Music Recording
Music recordings sounding flat? Adjust gain for dynamic instruments!
- Key Tips: Tailor gain to instrument dynamics (e.g., drums need more headroom, target -18dB peaks). Balance gain for multitrack recordings and use a compressor for control.
- Mic Placement: Experiment with angles for the best tone (e.g., place mic near guitar soundhole).
- Pro Tip: Dynamic mics excel for high-pressure instruments—avoid clipping.
Video Conferences and Online Teaching
Voice unclear in meetings? Optimize gain for crisp communication!
- Key Tips: Use software gain tweaks and noise suppression (like Zoom’s noise reduction), targeting -6dB peaks. Avoid feedback with earphones.
- Mic Placement: Keep a steady 8-inch distance to minimize movement noise.
- Pro Tip: Lock gain in meeting software for consistent clarity.
Troubleshooting Microphone Gain Issues
Running into recording problems? Here’s how to fix common gain issues:
- Distortion or Clipping: Gain too high. Lower to -18dB and use a pad if available.
- Weak Signal: Gain too low. Increase gain, checking mic type.
- Background Noise: Environmental interference. Use a noise gate and adjust mic distance (6-12 inches).
- Feedback Screech: Monitor volume too high. Turn off monitoring or use earphones.
- Software Glitches: Gain resets. Lock settings or update drivers.
Quick Tip: Still got issues? Double-check cables and power supply for hidden problems!
Conclusion
Proper microphone gain settings are the foundation of great audio, making your voice shine in podcasts, videos, or meetings. With this guide, you can dodge common pitfalls and fine-tune your setup for pro results. Practice makes perfect—test your gear, tweak settings, and keep learning audio tips to take your sound to the next level!
To learn more about the latest news from BOYA, join in our official social media accounts: Facebook, Youtube, Instagram.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the Ideal Microphone Gain Setting?
Aim for peaks between -18dB and -6dB, tweaking based on your gear and environment.
What’s the Difference Between Gain and Volume?
Gain boosts the input signal; volume controls output loudness.
Why Is My Mic Distorting?
Usually due to high gain causing clipping. Lower gain and check the signal chain.
How Can I Reduce Background Noise?
Optimize gain, use a noise gate, and improve your recording environment.
What Are the Best Tools for Beginners to Adjust Gain?
Try Audacity or OBS Studio’s built-in VU meters for easy real-time monitoring.































